






Pulmonary EmbolismEvaluationPulmonary EmbolismEvaluation
Adam Guttentag M.D.Adam Guttentag M.D.







The PE ParadoxThe PE Paradox
Very common disease—usually missedVery common disease—usually missed
Commonly considered clinical diagnosis—usually wrongCommonly considered clinical diagnosis—usually wrong
In other words…In other words…
In most patients with PE, we don’t think of thediagnosis and…In most patients with PE, we don’t think of thediagnosis and…
In most patients in whom the diagnosis ispursued, it is not present.In most patients in whom the diagnosis ispursued, it is not present.







Pulmonary EmbolismPulmonary Embolism
Large numbers of patients die of PELarge numbers of patients die of PE
3rd most common cause of death3rd most common cause of death
650,000 deaths per year650,000 deaths per year
70% of PE found at autopsy was not suspected pre-mortem.70% of PE found at autopsy was not suspected pre-mortem.
1/3 who survive initial event will die of PE in thefuture. Mortality much less in treated patients.1/3 who survive initial event will die of PE in thefuture. Mortality much less in treated patients.
Many hospitalized patients have unsuspected DVT.Many hospitalized patients have unsuspected DVT.
You must think of the diagnosis in order to make it.You must think of the diagnosis in order to make it.







Problems with clinical evaluation Problems with clinical evaluation
Symptoms and signs are very nonspecificSymptoms and signs are very nonspecific
Classic sx: chest pain, dyspnea, hemoptysisClassic sx: chest pain, dyspnea, hemoptysis
not always presentnot always present
Non-classic sx: syncope, wheezing, arrhythmiaNon-classic sx: syncope, wheezing, arrhythmia
Labs not helpfulLabs not helpful
Hypoxia not a reliable findingHypoxia not a reliable finding
Degree of hypoxia not proportional to extent of PEDegree of hypoxia not proportional to extent of PE
Elevated WBC commonElevated WBC common
Classic ECG findings in only 20%Classic ECG findings in only 20%
Dozens of differential dx’sDozens of differential dx’s







Radiologic EvaluationRadiologic Evaluation
Most work ups for DVT/PE are negativeMost work ups for DVT/PE are negative
At best, about 1/3 of PE workups will be positive.At best, about 1/3 of PE workups will be positive.
With easy availability of MDCT in ERs, manyhospitals have positive rate of <20%.With easy availability of MDCT in ERs, manyhospitals have positive rate of <20%.







Radiologic EvaluationRadiologic Evaluation
“Gestalt” evaluation of likelihood of PE is good, butnot adequate, even with experienced MDs.“Gestalt” evaluation of likelihood of PE is good, butnot adequate, even with experienced MDs.
Use pretest probability systems, especially ifinexperienced residents are making workup decisions.Use pretest probability systems, especially ifinexperienced residents are making workup decisions.
Geneva, Wells criteriaGeneva, Wells criteria
Have a standardized protocol for evaluating patientswith possible PE.Have a standardized protocol for evaluating patientswith possible PE.







Pulmonary ThromboembolismImaging QuestionsPulmonary ThromboembolismImaging Questions
Is it reasonable to image everyone in whom thediagnosis is raised?Is it reasonable to image everyone in whom thediagnosis is raised?
How do we improve our patient selection toavoid over-utilizing expensive imaging?How do we improve our patient selection toavoid over-utilizing expensive imaging?
What imaging modalities are available?What imaging modalities are available?
Varies by institutionVaries by institution
What is the best use of various imagingmodalities?What is the best use of various imagingmodalities?







DVT / PE ImagingDVT / PE Imaging
Chest X-rayChest X-ray
Nuclear V/Q scanNuclear V/Q scan
CT pulmonary arteriogram (CTPA)CT pulmonary arteriogram (CTPA)
Doppler Ultrasound of legsDoppler Ultrasound of legs
MR AngiographyMR Angiography
Conventional Pulmonary AngiogramConventional Pulmonary Angiogram







Chest X-rayChest X-ray
Essential first step in imagingsequence.Essential first step in imagingsequence.
Rule in other causes of symptoms:Rule in other causes of symptoms:
Pneumothorax, CHF, pneumonia, etcPneumothorax, CHF, pneumonia, etc
Can be used to guide sequence oftests for PE.Can be used to guide sequence oftests for PE.
Signs of PE:Signs of PE:
Regional oligemia (rare)Regional oligemia (rare)
Platelike atelectasis (common)Platelike atelectasis (common)
Elevated hemidiaphragmElevated hemidiaphragm
Localized consolidation (Hamptonhump)Localized consolidation (Hamptonhump)







Doppler UltrasoundDoppler Ultrasound
Advantages:Advantages:
Highly accurate forevaluation of femoral andpopliteal veinsHighly accurate forevaluation of femoral andpopliteal veins
RapidRapid
InexpensiveInexpensive
Disadvantages:Disadvantages:
No evaluation of PENo evaluation of PE
Limited in very obesepatientsLimited in very obesepatients
Operator dependentOperator dependent







Nuclear V/Q scanNuclear V/Q scan
Advantages:Advantages:
RapidRapid
High prob and normalscans reliable in mostpatientsHigh prob and normalscans reliable in mostpatients
Requires little patientcooperation.Requires little patientcooperation.
No contrast.No contrast.
Disadvantages:Disadvantages:
Indirect imaging ofvessels.Indirect imaging ofvessels.
Not available 24/7everywhere.Not available 24/7everywhere.
Intermediate prob scannot much help.Intermediate prob scannot much help.
Low prob not much helpin patient with highsuspicion.Low prob not much helpin patient with highsuspicion.








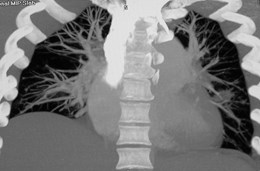
CT AngiographyCT Angiography
Advantages:Advantages:
Multislice technologywidely availableMultislice technologywidely available
RapidRapid
AccurateAccurate
Direct imaging of vesselsDirect imaging of vessels
Can add venography withsame injection to evaluatethe legs and central veinsCan add venography withsame injection to evaluatethe legs and central veins
Disadvantages:Disadvantages:
Requires contrast injectionRequires contrast injection
Renal function, allergiesRenal function, allergies
Radiation dose highRadiation dose high
Requires breath hold of 8-18 seconds for bestaccuracyRequires breath hold of 8-18 seconds for bestaccuracy







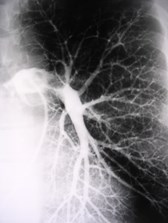
Conventional AngiographyConventional Angiography
Advantages:Advantages:
“Gold standard”“Gold standard”
Direct imaging of vesselsDirect imaging of vessels
High sensitivityHigh sensitivity
High confidence innegative testHigh confidence innegative test
Disadvantages:Disadvantages:
InvasiveInvasive
Small but real risksSmall but real risks
5% morbidity, <1%mortality5% morbidity, <1%mortality
Poor interobserver agreementfor smaller vesselsPoor interobserver agreementfor smaller vessels
Requires specializedpersonnel, equipmentRequires specializedpersonnel, equipment
Limited availabilityLimited availability







MR AngiographyMR Angiography
Advantages:Advantages:
No radiationNo radiation
No iodinated contrastNo iodinated contrast
(requires contrast, though)(requires contrast, though)
Direct imaging of vesselsDirect imaging of vessels
RapidRapid
Disadvantages:Disadvantages:
Limited availabilityLimited availability
Requires contrastinjectionRequires contrastinjection
Critically ill patientsrequire special ventilator,monitoring equipmentCritically ill patientsrequire special ventilator,monitoring equipment







PE: Radiologic workupPE: Radiologic workup
Einstein algorithmEinstein algorithm







Patient with suspected
PE / DVT
Chest x-ray normal?
Bun/Creat abnormal?
Contrast Allergy?
Can’t hold breath?
DVT Sx?
inter
high
normal
No
further eval
for PE
low
CT
PAgram
Venous
Doppler
US
yes
no
V/Q
scan
yes toany
+
Treat
+
+
Venous
Doppler
US
_
_
no
_







V/Q scanV/Q scan
PIOPED study established standardized criteriafor assigning likelihood of PEPIOPED study established standardized criteriafor assigning likelihood of PE
True likelihood depends on pretest assessmentof likelihood of PETrue likelihood depends on pretest assessmentof likelihood of PE
High prob V/Q + low risk pt = 50% chance of PEHigh prob V/Q + low risk pt = 50% chance of PE
Low prob V/Q + high risk pt = 16% chance of PELow prob V/Q + high risk pt = 16% chance of PE
At AEMC, V/Q performed as first test if CXRnormal and no COPDAt AEMC, V/Q performed as first test if CXRnormal and no COPD
Intermediate probability scan in only 11%.Intermediate probability scan in only 11%.







V/Q scanV/Q scan
Perfusion scan: microembolization ofpulmonary vascular bed with labeled aggregatesof albuminPerfusion scan: microembolization ofpulmonary vascular bed with labeled aggregatesof albumin
Ventilation scan: may be performed withTechnicium labeled DTPA aerosol or Xenon gasVentilation scan: may be performed withTechnicium labeled DTPA aerosol or Xenon gas
Fetal dose similar to CTPAgram in pregnantpatientsFetal dose similar to CTPAgram in pregnantpatients








Normal V/Q scanNormal V/Q scan
ventilation
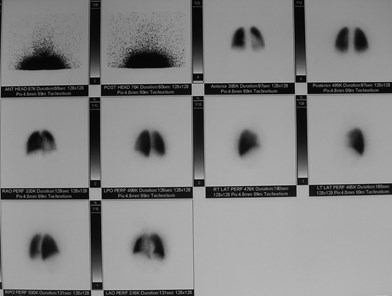
perfusion







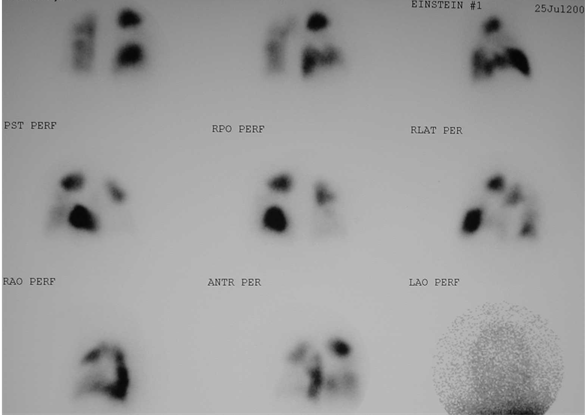
High probability V/Q scanHigh probability V/Q scan







CT PAgram - TechniqueCT PAgram - Technique
Best on modern multidetector CTBest on modern multidetector CT
4, 8 or 16 channels4, 8 or 16 channels
Scan at thinnest slice width possible for breath holdScan at thinnest slice width possible for breath hold
1mm best-good evaluation of most subsegmental vessels1mm best-good evaluation of most subsegmental vessels
2.5 - 3 mm satisfactory for segmental vessels2.5 - 3 mm satisfactory for segmental vessels
High injection rate of contrast for maximum vesselenhancementHigh injection rate of contrast for maximum vesselenhancement
3-4 cc/sec3-4 cc/sec
Breath hold 8 sec for 16 channel scanner, 18 sec for 4channelsBreath hold 8 sec for 16 channel scanner, 18 sec for 4channels
Window and levels settings customized to scanWindow and levels settings customized to scan







CT PAgramCT PAgram
How good is good enough?How good is good enough?
Respiratory motion, lung disease, poor enhancementmay limit evaluation of small vesselsRespiratory motion, lung disease, poor enhancementmay limit evaluation of small vessels
If only segmental vessels are well seen, and scanis normal, can the workup stop?If only segmental vessels are well seen, and scanis normal, can the workup stop?
What is the risk of missing subsegmentalembolism?What is the risk of missing subsegmentalembolism?
Isolated subsegmental PE in 6-30% of cases.Isolated subsegmental PE in 6-30% of cases.







CT PAgramCT PAgram
Follow up studies have shown that there is lowrisk of embolism in 6-12 months followingnegative CT evaluation.Follow up studies have shown that there is lowrisk of embolism in 6-12 months followingnegative CT evaluation.
Important to include a study of the legs.Important to include a study of the legs.
Any subsegmental emboli missed are probablyclinically insignificant in most patients.Any subsegmental emboli missed are probablyclinically insignificant in most patients.
Remember that conventional angiography maynot be reliable for small vessels.Remember that conventional angiography maynot be reliable for small vessels.







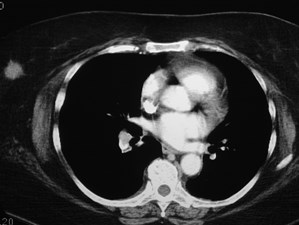
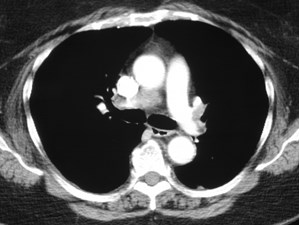
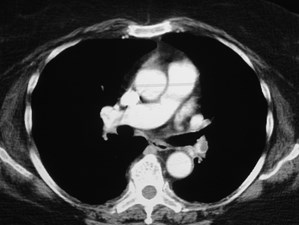
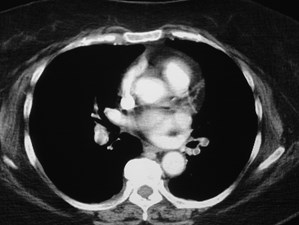
Positive CTPA—Acute PEPositive CTPA—Acute PE







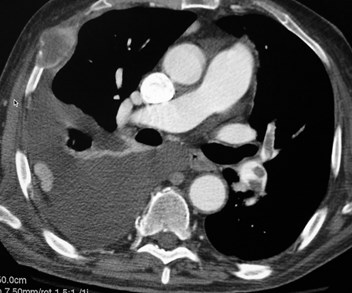
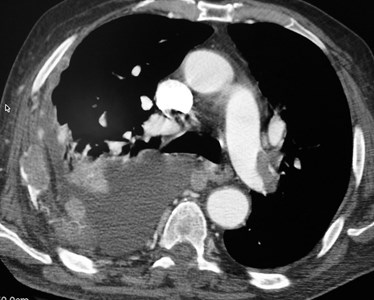
Acute PEAcute PE







Signs of massive embolismSigns of massive embolism
Clinical: loud P2, JVD—signs of RV failure, PAHTNClinical: loud P2, JVD—signs of RV failure, PAHTN
Dilated Main PA and right ventricleDilated Main PA and right ventricle
Reflux of contrast into IVCReflux of contrast into IVC
Straightening of IV septum or bowing towardsLV lumenStraightening of IV septum or bowing towardsLV lumen







Massive PE with right heart failureMassive PE with right heart failure
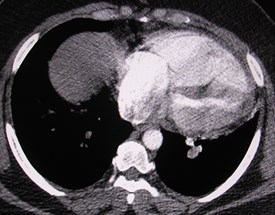
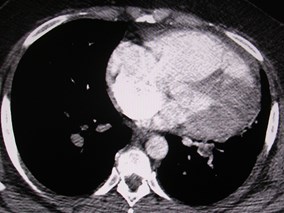
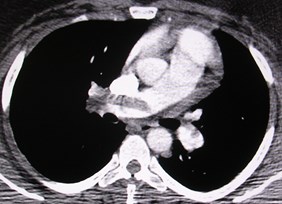
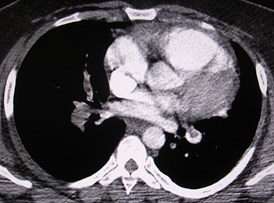







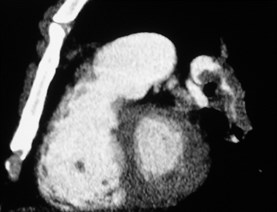
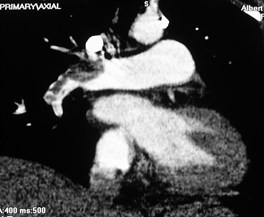
MPR may help define PEMPR may help define PE
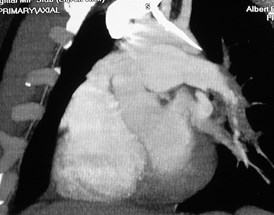
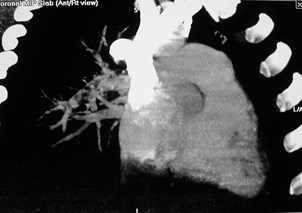
Thick slab MIP







Pulmonary infarctionPulmonary infarction
Not commonNot common
Bronchial arteries usually supply sufficient flowBronchial arteries usually supply sufficient flow
Generally found with coexisting LV dysfunction,pulmonary venous HTNGenerally found with coexisting LV dysfunction,pulmonary venous HTN
Peripheral consolidation broadly based on pleuraPeripheral consolidation broadly based on pleura
“melting snowball” over several days to weeks“melting snowball” over several days to weeks
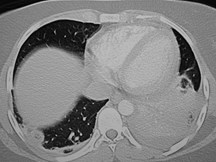
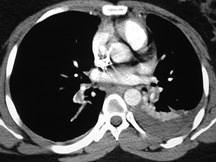







Chronic PEChronic PE
Cause of chronic pulmonary hypertension, dyspneaCause of chronic pulmonary hypertension, dyspnea
May not have known hx of acute PEMay not have known hx of acute PE
Most acute PE resolves without residuaMost acute PE resolves without residua
CT findings:CT findings:
Crescentic thrombus along wall of vessels, not in centerCrescentic thrombus along wall of vessels, not in center
Rapid tapering of vessels, small sizeRapid tapering of vessels, small size
Webs, irregular flapsWebs, irregular flaps
CalcificationCalcification







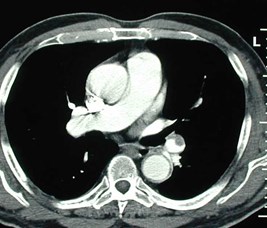
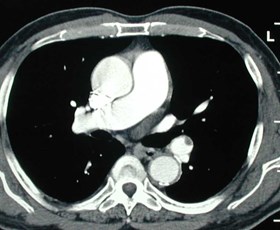
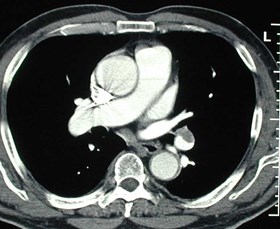
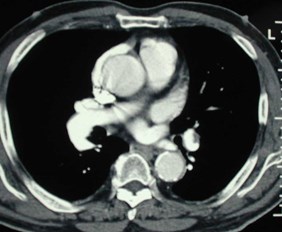
Chronic PEeccentric wall thickening, obtuse anglesChronic PEeccentric wall thickening, obtuse angles







Chronic PEcalcified organized thrombusChronic PEcalcified organized thrombus
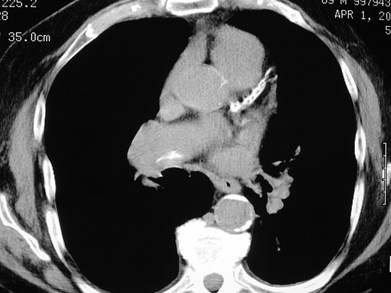







Chronic PEwebChronic PEweb
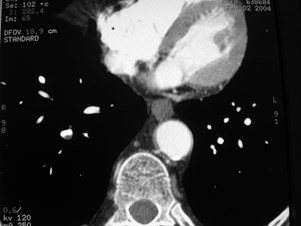
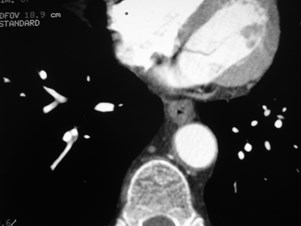
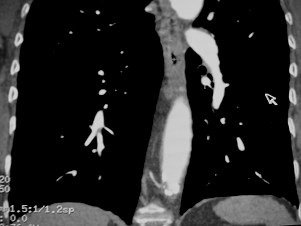







Acute on Chronic PEAcute on Chronic PE
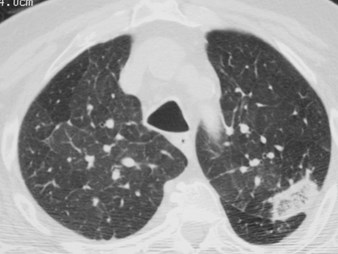
Pulmonary infarcts with mosaicoligemiaPulmonary infarcts with mosaicoligemia
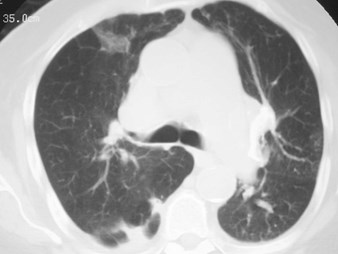







False Positive DiagnosisFalse Positive Diagnosis
ArtifactArtifact
Cardiac motion—stair step artifactCardiac motion—stair step artifact
Respiratory motionRespiratory motion
Volume averagingVolume averaging
Quantum mottleQuantum mottle
SVC streakingSVC streaking
Mucus pluggingMucus plugging
Chronic PEChronic PE
Hilar lymph nodesHilar lymph nodes
Veins poorly opacifiedVeins poorly opacified
Flow artifacts—unopacified blood entering from IVCFlow artifacts—unopacified blood entering from IVC







Mucous pluggingMucous plugging
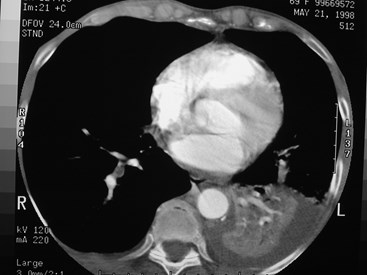
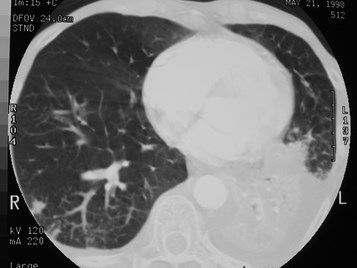







Windowing is important!Windowing is important!
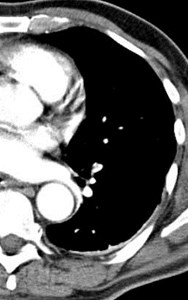
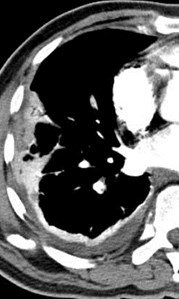
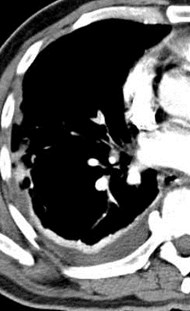
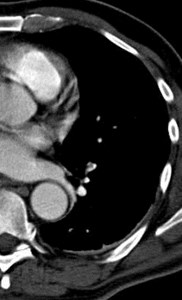
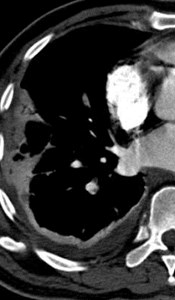
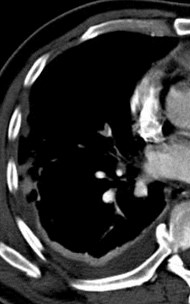







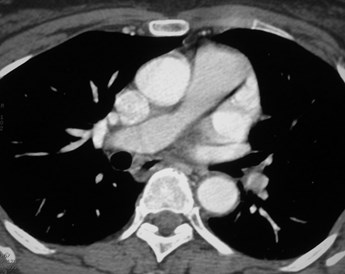
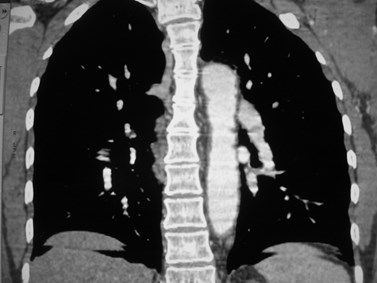
Positive for PE?Positive for PE?
“stair-step” artifact“stair-step” artifact







What’s new?What’s new?
D-dimer testingD-dimer testing
CT VenographyCT Venography
MRA?MRA?







D-dimerD-dimer
Doorkeeper testDoorkeeper test
Inexpensive, rapidInexpensive, rapid
Newer assays are quantitative, highly sensitiveNewer assays are quantitative, highly sensitive
High negative predictive valuesHigh negative predictive values
Negative test essentially precludes the presence ofDVT or PE.Negative test essentially precludes the presence ofDVT or PE.
Only in low or intermediate risk patientsOnly in low or intermediate risk patients
High risk patients may have PE even with negatived-dimer.High risk patients may have PE even with negatived-dimer.







Suggested protocol toinclude D-dimertestingSuggested protocol toinclude D-dimertesting







Patient with suspected PE
Low or intermediate risk
High risk
D-dimer
Proceed with
standard algorithm
No evaluation
for PE
-
+







CT VenographyCT Venography
Wait 2-3 minutes after CT PAgram.Wait 2-3 minutes after CT PAgram.
Scan every 4-5 cm from diaphragmto knees.Scan every 4-5 cm from diaphragmto knees.
Easy to identify most DVTEasy to identify most DVT
“one stop shopping” for PE andDVT evaluation“one stop shopping” for PE andDVT evaluation
Compares well in accuracy withDoppler USCompares well in accuracy withDoppler US
No additional contrast. Minimalextra time of exam.No additional contrast. Minimalextra time of exam.
Loud et al Radiology 2001;219:498-502Loud et al Radiology 2001;219:498-502
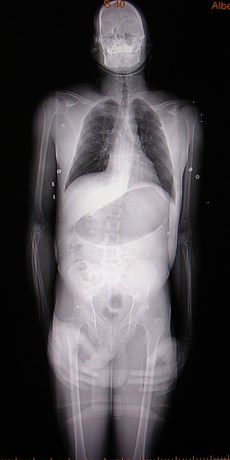







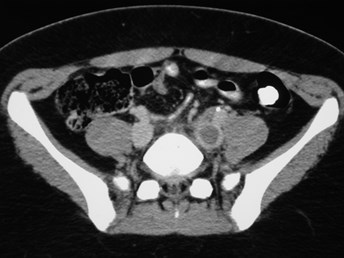
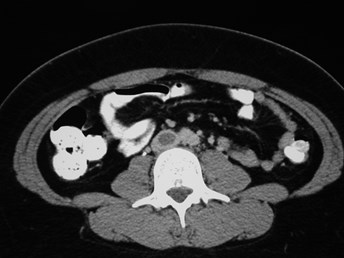
CT VenogramCT Venogram
IVC thrombus
Left iliac veinthrombus







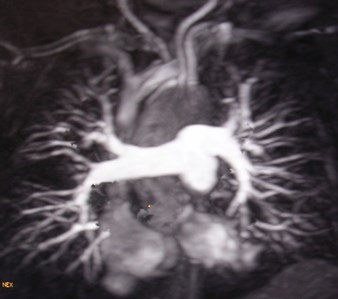
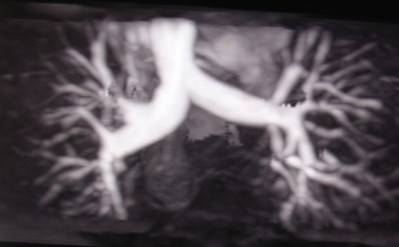
MR AngiographyMR Angiography







SummarySummary
Initial test:Initial test:
US if sx of DVTUS if sx of DVT
Choice of V/Q or CTPA depends on yourinstitution.Choice of V/Q or CTPA depends on yourinstitution.
V/Q only for patients with normal CXR orcontraindication to CTPAV/Q only for patients with normal CXR orcontraindication to CTPA
Secondary test:Secondary test:
If initial test is non-diagnosticIf initial test is non-diagnostic
Repeat CTPARepeat CTPA
Catheter angiographyCatheter angiography







